In today’s interconnected world, a stable and reliable Wi-Fi connection is crucial for Mac users to stay connected and productive. However, there may be instances when your Mac refuses to connect to Wi-Fi networks, leaving you frustrated and disconnected. In this article, we will explore the common reasons why your Mac may not be connecting to Wi-Fi and provide troubleshooting steps to help you resolve the issue.
1. Signal Interference
One of the primary reasons for a Mac’s Wi-Fi connectivity issues is signal interference. Various devices and objects, such as other wireless devices, walls, and even appliances, can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal, leading to a weak or unstable connection. Here’s what you can do to mitigate signal interference:
- Position your Mac closer to the Wi-Fi router: This helps to minimize the distance between your Mac and the router, improving signal strength.
- Reduce interference from other devices: Move other wireless devices away from your Mac, as their signals can interfere with the Wi-Fi connection. Additionally, avoid placing your Mac near large metal objects or walls that can block the Wi-Fi signal.
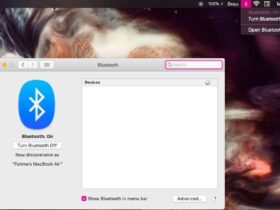
2. Network Settings
Misconfigured network settings can prevent your Mac from connecting to Wi-Fi networks. Here are a few troubleshooting steps you can take:
- Reset network settings: Go to “System Preferences” on your Mac, click on “Network,” and then select the Wi-Fi connection. Click on the minus (-) button to remove the network. Restart your Mac and add the network again to reset the network settings.
- Check for IP conflicts: In rare cases, IP conflicts can occur if multiple devices on the same network have the same IP address. To resolve this, assign a static IP address to your Mac or configure your router to use dynamic IP addresses.
3. Wi-Fi Router Issues
The problem may lie with your Wi-Fi router itself. Consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Restart your router: Unplug your router from the power source, wait for a few seconds, and then plug it back in. This simple step can resolve temporary glitches and connectivity issues.
- Update router firmware: Visit the manufacturer’s website to check for any firmware updates for your router. Updating the firmware can provide bug fixes and improve overall performance and compatibility.

- Modify router settings: Log in to your router’s administration panel and ensure that the Wi-Fi settings, such as the network name (SSID) and security settings, are correctly configured. Consult your router’s user manual or contact the manufacturer for specific instructions.
4. Wi-Fi Network Authentication
If you’re unable to connect to a specific Wi-Fi network, it might be due to authentication issues. Here’s what you can try:
- Verify network credentials: Double-check the network name (SSID) and password you’re using to connect to the Wi-Fi network. Ensure that they are entered correctly, paying attention to uppercase and lowercase letters.
- Forget and reconnect to the network: In the Wi-Fi settings on your Mac, select the network causing issues, and click on the minus (-) button to remove it from the known networks list. Then, reconnect to the network by selecting it from the list and entering the correct password.
5. Outdated Software
Outdated software on your Mac, including the operating system and Wi-Fi drivers, can contribute to connectivity problems. Here’s what you can do:
- Update macOS: Ensure that your Mac is running the latest version of macOS. Open the App Store, go to the “Updates” tab, and install any available updates.
- Update Wi-Fi drivers: Visit the Apple support website or the website of your Mac’s manufacturer to check for updated Wi-Fi drivers. Download and install the latest drivers to ensure optimal compatibility and performance.
6. Hardware Issues
In rare cases, hardware issues can be the cause of your Mac’s Wi-Fi connectivity problems. Here are a few steps to troubleshoot potential hardware issues:
the cause of your Mac’s Wi-Fi connectivity problems. Here are a few steps to troubleshoot potential hardware issues:
- Check Wi-Fi hardware: Ensure that the Wi-Fi hardware on your Mac is functioning properly. You can do this by going to “System Information” on your Mac, selecting “Wi-Fi” from the sidebar, and checking if the Wi-Fi hardware is detected and functioning without any errors.
- Reset the System Management Controller (SMC): The SMC is responsible for managing various hardware components on your Mac, including the Wi-Fi module. Resetting the SMC can help resolve hardware-related issues. The process to reset the SMC varies depending on your Mac model. Refer to Apple’s support documentation or contact Apple Support for instructions specific to your Mac.
- Consider professional assistance: If you’ve tried all the troubleshooting steps mentioned above and your Mac still doesn’t connect to Wi-Fi, it might be time to seek professional assistance. Contact Apple Support or visit an authorized service center to diagnose and repair any potential hardware issues.
7. Firewall or Security Software
Sometimes, your Mac’s firewall or third-party security software can interfere with Wi-Fi connections. Here’s what you can do:
- Disable firewall temporarily: Go to “System Preferences” on your Mac, click on “Security & Privacy,” and navigate to the “Firewall” tab. Disable the firewall temporarily and check if you can connect to the Wi-Fi network. If the issue is resolved, consider adjusting your firewall settings or adding exceptions for the necessary network ports.
- Check security software settings: If you have third-party security software installed on your Mac, check its settings to ensure that it is not blocking or interfering with Wi-Fi connections. Temporarily disable the security software and check if the issue persists. If disabling the software resolves the problem, consult the software’s documentation or contact their support for further assistance.
How to Connect Xbox Controller to Mac?
8. Seek Professional Assistance
If you have exhausted all the troubleshooting steps and your Mac still refuses to connect to Wi-Fi, it may be necessary to seek professional assistance. Apple Support or an authorized Apple service center can provide expert guidance and diagnose any underlying issues with your Mac’s hardware or software.
In conclusion, Wi-Fi connectivity issues on your Mac can be caused by various factors, including signal interference, network settings, router issues, authentication problems, outdated software, hardware issues, and firewall or security software conflicts. By following the troubleshooting steps outlined above, you can diagnose and resolve most common Wi-Fi connectivity problems on your Mac. Remember to keep your software and hardware up to date, and don’t hesitate to seek professional help when needed. Stay connected and enjoy a seamless Wi-Fi experience on your Mac!











Leave a Reply